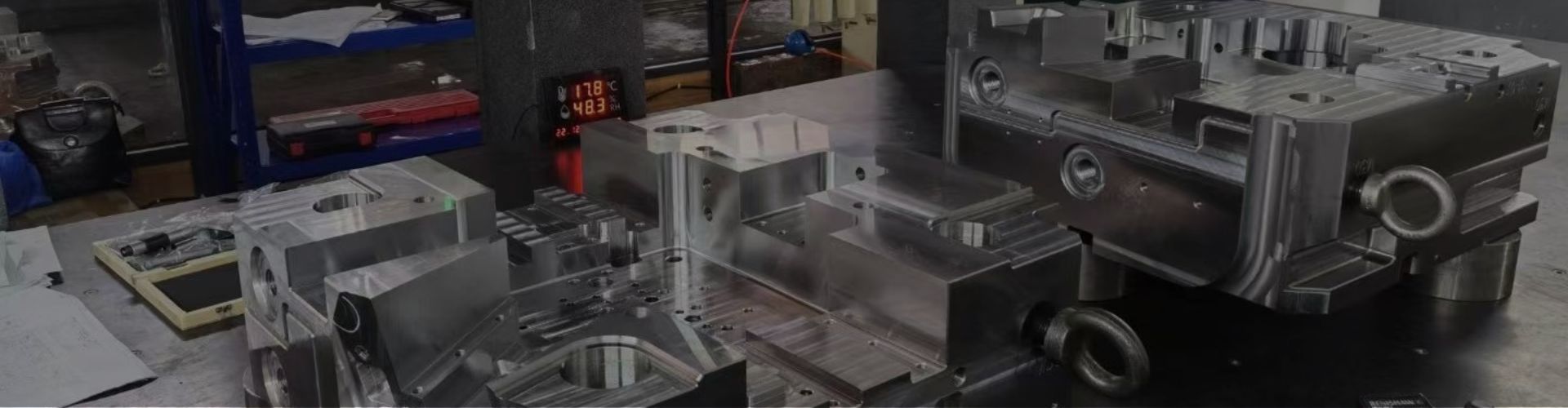
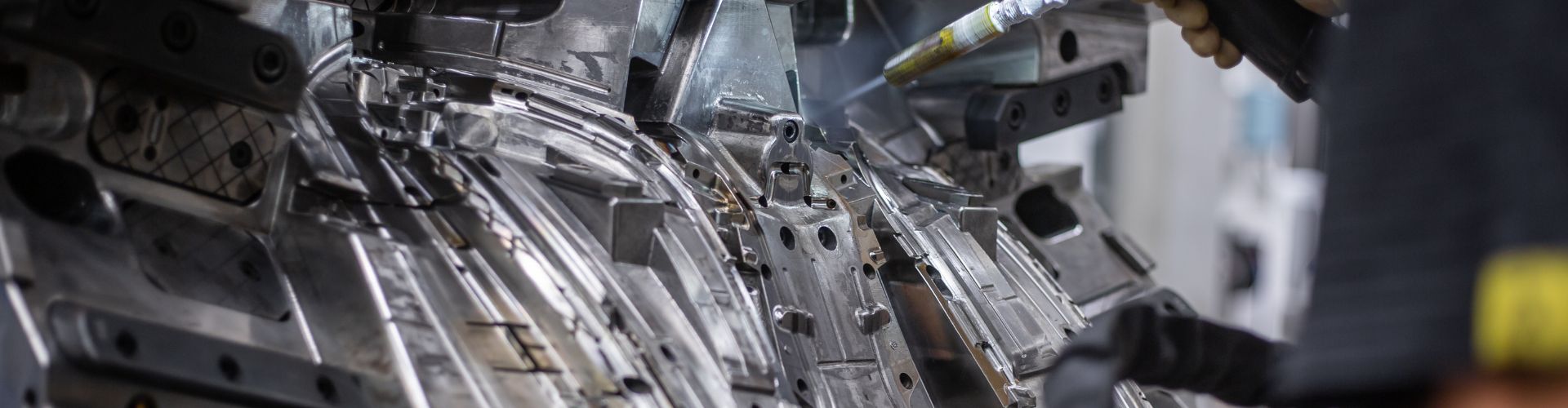
What is Die Casting Mould?
A die-casting mould is a tool made of high-quality steel that cooperates with a die-casting machine to solidify and shape metal alloy materials. It is assembled with mold foot, mold frame, mould cavities, and accessories. It has a moving half and a fixed half, the two halves are brought together internally to form a finished product shape.
The high-temperature molten metal liquid is injected into the cavity of the mold at high speed through the plunger of the die-casting machine, under pressure, and after cooling, we get the desired metal shape.
The quality of mould material and mould design decide the lifetime of the mould and the quality of the die-casting parts it makes.
The mold’s structure is critical to its performance and lifespan. Here are key factors to consider die casting mould design:
- Parting Surface: The parting surface should be well-placed to simplify the mold. Horizontal or vertical parting can enhance efficiency and simplify the mold structure.
- Runner and Gate Position: Ensure a straightforward position for the runner and gate, facilitating material feeding and exhaust. Optimal cross-sectional areas prevent unnecessary material wastage.
- Gate and Runner Removal: Make it easy to remove gates and runners, preferably by direct knocking rather than using a chainsaw, which can be time-consuming, labor-intensive, and may increase deburring costs.
- Material Shrinkage: Consider the shrinkage rate of different materials (usually 0.5%-1.5%) and account for variations among materials like aluminum alloys (lower shrinkage), magnesium alloys (higher shrinkage), and copper alloys (in-between). Thickness and product complexity also impact shrinkage.
- Ejector Rod Position: Ensure ejector rod positions avoid critical surfaces and assembly areas, use supporting positions, and avoid locations that are too thin, which could result in protrusions. The position of the ejector pin should be convenient for demoulding.
3. The mold’s complexity also affects its lifespan, with simpler structures generally enjoying a longer service life. Complex molds, especially those with deep and extensive heat dissipation ribs, are more prone to surface and junction cracks.
4. The role of skilled die-casting operators, proper mold usage, reasonable die-casting parameters (pressure and time), and other factors are crucial for the mold’s longevity:
- Cooling System: Utilize a cooling system during die casting to prevent overheating, cracks, product strain, and deformation. It reduces the need for release agents, shortens die-casting cycles, and enhances product quality.
- Pre-Heating: Preheat the mold before production to prevent thermal shock. More complex molds may require preheating using methods like a blowtorch, liquefied gas, or a mold temperature machine.
- Mold Cleaning: Regularly clean the mold’s parting surface to maintain product quality. Leftover flash or residue can disrupt the production process and pose safety hazards.
- Handling Running Aluminum: Address running aluminum promptly to avoid increased die-casting costs, product quality issues, and safety risks. Running aluminum can lead to decreased pass rates and higher injury risks.
- Shift Changes: Thoroughly clean the mold’s parting surface with kerosene during shift changes. This not only prevents mold damage but also improves gas discharge and product quality during the injection process.
- Vulnerable Parts: Inspect vulnerable components like ejector pins and cores for bends or cracks and replace them as needed.
- Polishing: Address areas with aluminum sticking and carbon deposits through minor polishing.
- Lubrication and Rust Prevention: Maintain lubrication and prevent rust on all moving parts, joints, screws, and other mold components.
- Regular Maintenance: Large molds require periodic maintenance, with maintenance records maintained in a ledger.
These practices are essential to ensure the mold’s longevity, product quality, and the safety of die-casting operations.
Die Cast Mould Making Process - Step by Step Guide
The production process of die-casting molds includes design and engineering, mold material procurement, material processing, precision machining, assembly, heat treatment, trial and adjustment, mold production, quality control, maintenance, and repairs. The mold manufacturing process is the specific transformation of mold design into physical mold products.
Following, we will explain step by step the production and processing of the die-casting mold’s cavities and mold frames, which involve mold CNC machining processes and specialized treatments.
- Mold machining processes encompass turning, milling, planing, grinding, boring, engraving, and more.
- Specialized mold treatments include EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining), wire cutting, chemical processing, polishing, heat treatment, laser engraving, and others.

The process of manufacturing molds typically begins with the mold design based on product part drawings or physical objects.
Once the mold design is completed, it will be submitted to the client for approval. After the client confirms the mold design, we can proceed with the mold production.
Mould design including: 3D drawing, mold flow analysis, and 2D drawings.

Based on the die-casting mold drawings confirmed by the client, the procurement of mold blank materials is carried out. The mold material supplier will submit a material certification. The lifespan of the mold is closely linked to the materials used.
- Frame Materials: Commonly used frame materials include 45C, 50C, 55C, QT550, QT600, and S50C.
- Mold Core Materials: Commonly used mold core materials include H13, Dievar, SKD61, DAC, DH-31, 8407, 8418, H13, 3Cr2W8V, 4Cr5MoSiV, 1.2344, and W302.

Upon the arrival of the mold materials at the factory and inspection qualified, the initial step will be carried out, it is the first round of rough milling.
- This process involves milling out the suitable space for placing the upper and lower mold cores on the mold frame materials.
- The designed product’s outer shape is approximately milled on the mold core material, with appropriate allowances for machining and heat treatment deformation residual based on the size of the mold dimensions.

Heat treatment and surface treatment processes are crucial for ensuring the quality and performance of molds. Mould cavity hardness after heat treatment is 45-52HRC, depending on the customer’s requirement, and the characteristics of the mold material itself.
- Through a series of heat treatment steps, including annealing, normalizing, quenching, and tempering, the mold’s frame and core are processed.
- The purpose of these heat treatments is to enhance the mechanical properties of the tool steel and the mold’s lifespan.

After heat treatment, the mold frame and core may undergo deformation.
- Use a planer and grinder to process the upper and lower surface of the mold frame and mould matrix cavity to achieve precise dimensions and parallelism on all four sides and corners, everything square.
- Use a double-head milling machine to mill the outer contour of the die-casting mould cavity core material straight and vertically.
The purpose is to ensure the smooth assembly of the mold cavity and mold frame.

Use the high-speed machining center to machining the cavity size as the drawing indicated.
- Tolerance around 0.05 mm-0.1 mm.
- The mold matrix’s internal precision is further refined.
- The machining allowances previously retained and any deformation resulting from heat treatment are addressed.
Through this secondary machining process, the mold’s precision is brought in line with the specifications outlined in the design drawings.

EDM machining utilizes electrodes to erode conductive materials through the erosive effect of pulse discharges between two electrodes immersed in a working fluid.
For the position that the machining center cannot process, we use copper and Graphite is processed by electric discharge treatment to the right size. Sinker EDM machining can achieve dimensions, depths, angles, and irregular complex shapes that are difficult to attain through conventional machining.

Wire EDM (Wire Electrical Discharge Machining), also known as wire cutting, is a specialized machining process. We employ wire-cutting to meticulously create ejection pinholes and inserts (blocks) with exceptional precision and accuracy.
WEDM proves particularly invaluable in the production of die-casting molds, tooling, and die-making, where strict tolerances and high precision are imperative.

At last, the mold’s surface undergoes meticulous hand polishing. Depending on the product’s surface requirements, certain molds can achieve a mirror-like finish.
Polishing serves to eliminate machining and EDM traces, and this smooth surface significantly aids in mold release, ultimately enhancing the overall efficiency of the molding process.
A time clock can be engraved inside the cavity for tracking purposes, if necessary.

With the trend towards more integrated die casting, the dimensions of molds and products are growing larger.
For die casting moulds larger than 800ton die casting machines, the use of a die-spotting press for aligning the two halves of molds significantly assists mold engineers in achieving better matching.
Mold accessories such as mold foot, punch, die, guide pillar, guide bushing, ejector pin, thimble, sleeve, steel ball sleeve, oil-free guide bushing, oil-free slide plate, guide pin components, and more will be assembled by workers.

Once the die casting mold is completed, a mold trial is conducted, which is a critical phase in mold production.
- The mold trial plan is prepared by the die-casting engineer and includes parameters such as temperature, flow rate, pressure, injection time, and holding time based on mold flow analysis and the engineer’s rich experience in die casting process.
- Die-casting operators then make on-site adjustments to fine-tune the mold’s performance, optimizing it for production. This process relies heavily on the experience of die-casting operators, and at Yontone, our trial operators have over 10 years of die-casting experience.
- The casting parameters and video recordings are documented and compiled into files for later batch production use.
Successful mold trials are essential to ensure that the mold is ready for mass production.

Die-cast products need to undergo machining and surface treatment before being submitted as final samples to the client.
- Material reports, dimension reports, performance reports, and other documents are prepared based on the client’s requirements.
- Mass production of the die-cast products can only commence after the client’s approval.
Yontone company also offers standalone die casting mold design and mould manufacture production services, providing high-quality molds with good quality, high efficiency, and long lifespan to various die-casting enterprises worldwide.
- Yontone’s engineering department is dedicated to helping customers resolve any issues they encounter during the die-casting process.
Advantages of Die Casting Mould
The product shape made by die-casting molds can be more complicated, the wall thickness can be changed, and one die-casting part can replace several sheet metal parts, thus simplifying the product structure.
Compared with plastic parts, metal parts made by die casting mould have advantages in terms of strength, electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and anti-electromagnetic radiation.
Compared with other casting methods (sand casting, gravity casting, low pressure casting), products made by die casting molds have higher dimensional accuracy, better surface quality, and higher production efficiency.
With slider side core pulling mechanism of die casting mould design, it can make more complicated parts with lower cost and higher degree of automation than the CNC machining process.
Reverse Engineering Ability
In the development and innovation of new products, many product data are not CAD digital models.
Mold designers are faced with physical samples, and sometimes drawings may be missing.
In this case, Yontone provides customers with 3D digitization and reverse engineering drawing design using 3D scanning technology. Provide intelligent solutions for design and manufacturing.
Self Die Casting Mold Design and Manufacturing
The parting line, ingate, runner, and cooling system in the high-pressure die casting mold design are all critically important elements. They influence injection time, closure time, and consequently, production time, which, in turn, affects production costs.
Yontone’s mold designer has at least 8 years of experience in aluminum alloy die-casting mold design and will use mold flow analysis to verify and optimize the designer’s mold design plan. Assisting clients in saving die-casting time, thereby reducing production costs.
Die Casting Mold Material and Heat Treatment
The material used for the mold cavity has a significant impact on both the mold’s lifespan and product precision. In the market, the price of hot working mold steel of the same grade can vary significantly, ranging from a few yuan to tens of yuan per kilogram. This cost difference can be substantial, reaching from a few thousand yuan to several hundred thousand yuan for a mold weighing several tons.
The choice of mold frame material and dimensions is also vital for the mold’s lifespan. Common mold frame materials include cast iron mold frames, 45C precision-milled mold frames, and 45C standard mold frames (also known as tempered mold frames, which undergo heat treatment for improved strength).
Yontone procures mold materials from reputable channels and large factories, all with qualified material reports, ensuring top-notch material quality.


Heat Treatment
Heat treatment is another critical factor influencing the mold’s lifespan. Proper heat treatment, involving quenching and tempering, results in a well-defined metallographic structure, appropriate hardness, excellent machinability, and increased surface hardness and toughness, significantly extending the mold’s lifespan.
Yontone takes heat treatment seriously, all mold cavities are sent to large heat treatment facilities to ensure the correct temperature and time.
Mould Making Workshop
Our high pressure permanent die casting mold making workshop is equipped with the most advanced machinery, including EDM, CNC milling machines, WEDM, and spotting machines.
These machines enable us to manufacture small and large die-casting molds ranging from 88 tons to 2000 tons.


Quality Control
All mold materials come with material reports.
All heat treatments are documented with heat treatment reports.
All mold core and frame dimensions are subjected to CMM inspections.
All die-casting materials are accompanied by material reports.
All die-casting samples are inspected using CMM.
Cold Chamber vs Hot Chamber Die Casting Mould


Die-casting machines are divided into hot-chamber and cold-chamber die-casting machines. Hot chamber die-casting machines are primarily used for zinc alloys, while cold chamber die-casting machines are mainly used for aluminum alloys, magnesium alloys, and brass alloys.
- Zinc alloys (zamak alloy), have lower melting points, die casting temperatures of over 400 degrees, a small solidification temperature range, and are easy to fill for molding. They exhibit minimal shrinkage tendencies and are suitable for die-casting complex, thin-walled precision parts with smooth surfaces and high dimensional accuracy. The lower casting temperature contributes to longer mold lifespans, reduced sticking to molds, and minimal mold corrosion.
- Aluminum(aluminum) alloys and magnesium Alloy have higher melting points, and die casting temperatures of around 700 degrees and offer excellent die-casting, electrical conductivity, and thermal conductivity properties, along with good machinability. However, aluminum-silicon series alloys tend to stick to molds, corrode metal crucibles, exhibit significant volume shrinkage, and can develop shrinkage porosity. While magnesium alloy is combustible, especially in powder form.
- Brass alloy has higher melting points, and die casting temperature of 900-1020 degrees. It has excellent thermal conductivity, electrical conductivity, and corrosion resistance.
Due to the differences in working principles and melting points of the metals used in these two types of machines, various aspects of die design, including the choice of mold materials, runner and gate design, product shrinkage rates, and draft angles, differ. At Yontone, the design of aluminum alloy die-casting molds is handled by cold chamber die-casting mold designers, while the design of zinc alloy die-casting molds is entrusted to hot chamber die-casting mold designers. Each specializes in their respective areas, ensuring that professional mold designers can create molds that are precise in dimensions, high in production efficiency, and have a high yield rate.
Why Choose Yontone to Be Your Die Casting Mould Manufacturing Company


Yontone is a 35-year professional mold-making company with aspirations and hopes to last for more than a hundred years, based on integrity. Provide after-sales service support and mold accessories support for life.
1. When choosing a high-quality mold steel material, Yontone considers not only its alloy composition but also the smelting process of the material. Choose mold steel with good thermal stability, the hardness will not decrease when it is just working at high temperature, and the thermal fatigue performance is good. When working in extremely cold and extremely hot environments, the mold will not crack or be eroded. Greatly improve the service life of the mold.
2. Our mold designer is a professional designer who has been engaged in the design of aluminum alloy die-casting molds for many years. At the same time, they have production experience in die-casting and machining. With the assistance of mold CAD and CAM software, he can design aluminum alloy die-casting molds with high efficiency and good structure. , Reduce material loss during die casting.
3. According to the size of the product and the size of the customer’s die-casting machine, reasonably calculate the number of cores and dimensions of the mold. Under the condition of ensuring that the mold is strong and durable, use reasonable materials and mold size to achieve a very cost-effective mold price.
4. Delivery time: the usual die-casting mold, according to the size of the product, the number of cores, and the size of the mold, the delivery time ranges from 35-65 days. If the customer needs to expedite, communicate with Yontone in advance, it can be two weeks shorter than the normal lead time.
What makes Yontone different?
In summary, high-pressure die casting molds produced with high-quality materials and meticulous heat treatment are usually of superior quality. However, they are also more expensive.
Yontone primarily focuses on cost considerations from the customer’s perspective and evaluates each project to recommend the most suitable material configuration based on the specific project.
- Low Volume: Not every customer needs molds with an exceptionally long lifespan, especially for die-casting projects with low precision requirements and small order quantities. In such cases, Yontone suggests cost-effective mold design and production solutions based on the client’s order information and predictions. Ensuring reasonable quality while controlling material and production costs to minimize the customer’s procurement expenses. For instance, non-industrial die-cast products with low demand and precision requirements can benefit from domestically sourced mold materials that offer good performance at a moderate price, resulting in cost savings for the customer.
- High Volume: Conversely, for high-volume die-casting production parts like automotive components and power tools parts, where precision requirements are high, we invest efforts in improving mold material performance and lifespan. Our aim is to provide customers with molds of superior quality, efficiency, and higher production capacity at a similar price. For such customers, we recommend using standard mold frames and high-performance imported mold steel materials. While high-quality standard mold frames may have an initially higher cost, they are exceptionally durable. In general, even after replacing the core 2-3 times, the original mold frame remains usable. Yontone also offers core replacement services, helping clients reduce procurement costs, and allowing clients to achieve the production capacity of three molds for the price of two.
Yontone’s idea is that while expensive molds are certainly good, offering high-quality die-casting molds with cost-effective solutions is even better. Our goal is to meet your needs while maximizing cost control.
Wild Application Fields of Die Casting Molds

Die-casting molds are widely used in the city lighting industry.
These molds are used to manufacture various metal components for lamps and streetlights to ensure their quality and durability. Common applications of die casting molds in this industry include lampshades and lamp bodies for streetlights, courtyard lights, factory lights, lamp bases and brackets, heat sinks and radiators, streetlight brackets and arms, and more.
Yontone’s designed and produced lighting housing and fixture shell molds are known for their high lifespan, high yield, and high production efficiency, earning consistent praise from customers.

The use of die-cast parts in the automotive and motorcycle industry is extensive due to their advantages of being lightweight, high-strength, and versatile in shape. In recent years, the trend of integrated die-casting has become increasingly prominent in the automotive parts sector. Integrated die-casting involves designing several adjacent components as a single unit, significantly reducing assembly costs. This is a process that cannot be easily accomplished through traditional methods like stamping and machining.
The shift towards integrated die-casting has led to larger dimensions in automotive parts, necessitating the use of larger die-casting molds. Common die-casting molds in the automotive sector are used for producing various components such as cylinder heads, crankcases, engine blocks, crankshafts, connecting rods, suspension arms, steering columns, suspension nodes, door handles, center consoles, steering wheels, alloy wheel hubs, battery enclosures, outer casings for electronic control modules, brake discs, and brake calipers.
Yontone has accumulated years of experience in designing and manufacturing large aluminum die-casting molds for automotive components. We are committed to providing durable and cost-effective mold services to meet the evolving demands of the automotive parts market.

Die-casting molds have widespread applications in the fields of office furniture and home furnishings.
These molds are utilized for manufacturing various metal and alloy components to produce office furniture and household items. The following are common applications of die-casting molds in these domains: metal components for office desks and swivel chairs, brackets, chair frames, connectors, furniture handles, leg stands, metal brackets for TVs and audio equipment, and more.
Yontone boasts years of experience in die-casting mold design and production, providing high-quality metal components to meet the needs of manufacturers in the office furniture and furniture industries.

The metals used in the aerospace industry need to possess high strength, corrosion resistance, and high-temperature stability. Commonly used metal alloys include titanium alloys, aluminum alloys, stainless steel, nickel-based alloys, and more.
Die-casting molds have extensive applications in this field. They are used for manufacturing engine components, flight controllers, cabin structures, seat parts, aircraft outer shells, rocket components, space probes, satellite parts, and other related components. These include seat brackets, instrument panel brackets, wall panels, electronic control boxes, sensor casings, communication equipment casings, fuel pump housings, nozzles, combustion chambers, and more.
Yontone has years of experience in die-casting mold design and production for aerospace components, assisting customers in the mass production of these products.

Die-casting molds find applications in the field of new energy. They are used to manufacture various components for solar energy, wind turbines, electric vehicles, and energy storage systems. These applications include solar panel brackets, solar reflectors, wind turbine parts such as blade brackets, bearing seats, and turbine casings, battery housings for electric vehicles and energy storage systems, brackets and frameworks for biomass power generation and biofuel equipment, components for electric vehicles including motor housings, battery brackets, and charging device parts, as well as die-castings for battery management systems, including controller housings, connectors, and heat sinks.
Yontone excels in die-casting molds for various housing and bracket types with heat sinks. Through our mold design and manufacturing expertise, we assist clients in producing high-strength, high-performance, and durable components to meet the demands of the new energy sector.

Die-casting molds play a vital role in the production of components for electric tools. These molds are used to manufacture various metal parts and components for electric tools, ensuring their quality, precision, and durability. Some common applications of die-casting molds in the electric tool industry include manufacturing metal housings, handles, motor casings, gearboxes, brackets, and various other parts that are essential for the functionality and performance of electric tools.
Yontone has extensive experience in designing and manufacturing die-casting molds for electric tool components, helping manufacturers in this industry produce high-quality and reliable parts to meet the needs of their products.











